About:
Spring-1:
Enables Plain Old Java
Object (POJO) based programming model with POJO you don’t need EJB container
product utilizes existing technologies like ORM frameworks logging frameworks JEE,
Quartz, JDK timers.
Spring-2:
It is a well-designed
web model-view-controller (MVC) framework (a great alternative to Struts) provides
a coherent transaction management interface that be applicable to a local transactions
() local transactions or global transactions (JTA) provides a suitable API for
translating technology-specific exceptions (for instance, thrown by JDBC,
Hibernate, or JDO,) into consistent, unchecked exceptions. The Inversion of
Control (IoC) containers are lightweight, especially when compared to EJB containers.
Being lightweight is beneficial for developing and deploying applications on
computers with limited resources (RAM&CPU). Testing is simple because
environment-dependent code is moved into this framework.
Beans?
In spring, POJO’s (plain old java object)
are called ‘beans’ and those objects instantiated, managed, created by Spring
IoC container. Beans are created with the configuration metadata (XML file)
that we supply to the container. Bean
definition contains configuration metadata. With this information container
knows how to create bean, beans lifecycle, beans dependencies After
specifying objects of an application, instances of those objects will be
reached by getBean() method. Spring supports given scope types for beans:
Singleton (a single
instance per Spring IoC container (default))
Prototype
Request
Session
Global-session
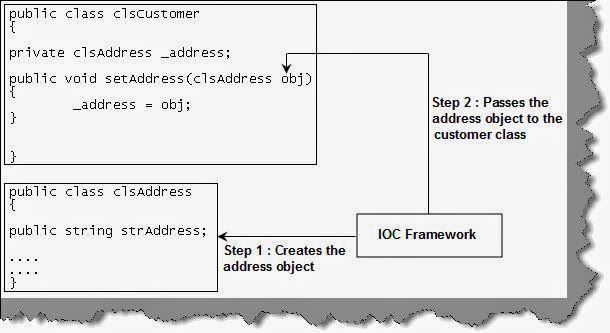 The BeanFactory interface provides an
advanced high level configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of
objects. BeanFactory provides configuration level basic functionality for IoC
implementation.
The BeanFactory interface provides an
advanced high level configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of
objects. BeanFactory provides configuration level basic functionality for IoC
implementation.ApplicationContext is a sub-interface that is built on BeanFactory, it provides application level context to be used in Spring web applications. ApplicationContext is a complete super-set of BeanFactory and any functionality provided by BeanFactory is also available in ApplicationContext.
Spring configuration contains at least one bean definition that the container must manage. These beans are declared under
Packages,
Classes and Interfaces (Spring IoC):
org.springframework.beans
and org.springframework.context are two packages that contains basic
functionality of Spring’s IoC.
Configuring
Beans:
IoC container consumes
some sort of configuration mostly in the form of XML, this configuration tells the
container a way in which the objects are to be instantiated, configured and
managed in the application.




No comments:
Post a Comment
I'm certainly not an expert, but I'll try my hardest to explain what I do know and research what I don't know.